Percutaneous occlusion of the left atrial appendage (LAA) for the prevention of thromboembolism in patients with atrial fibrillation.
Why do patients with atrial fibrillation have strokes?
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the irregular and rapid beating of the upper two chambers of the heart (the atria). It can cause symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness and breathlessness. People with AF have an increased risk of blood clots forming in the heart that may leave the heart and block a blood vessel in the brain causing a stroke. The major cause of serious disability and death in patients with AF is stroke. The annual stroke rate varies from 2% to more than 20% depending on the age and other illnesses of the patients. The clots that result in strokes originate in the atria, and the vast majority (>90%) of these arise in a small pocket off the left atrium called the left atrial appendage (LAA).
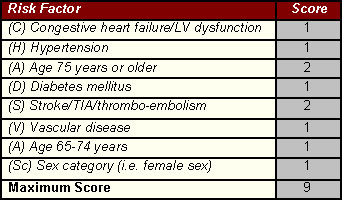
A number of factors have been identified that increase the clinical risk of stroke in patients with non-valvular AF. This scoring system has been referred to as the an acronym, CHA2DS2-VASc [congestive heart failure, hypertension, age ≥75 (doubled), diabetes, stroke (doubled), vascular disease, age 65–74, and sex category (female)]. This scheme is based on a point system in which 2 points are assigned for a history of stroke or TIA, or age ≥75; and 1 point each is assigned for age 65–74 years, a history of hypertension, diabetes, recent cardiac failure, vascular disease (myocardial infarction, complex aortic plaque, and peripheral arterial disease (PAD), including prior revascularization, amputation due to PAD, or angiographic evidence of PAD, etc.), and female sex (See table). Follow-up of over 7300 patients with AF has demonstrated the validity of this risk scoring system. The risk of stroke increases as the CHA2DS2-VASc score increases.
The blood clots that result in strokes originate in the atria, and the vast majority (>90%) of these arise in a small pocket off the left atrium called the left atrial appendage (LAA). To prevent stroke one can either take drugs to prevent the blood clots from forming (oral anticoagulants, OAC) or remove the site where the clots form in the heart, the LAA.
Current UK National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) guidelines recommend oral anticoagulants ("blood-thinners") as the mainstay of therapy to reduce stroke risk in patients with AF, according to the risk of the patient
['Major' risk factor = Previous stroke, TIA, or systemic embolism; Age > 75 years. 'Clinically relevant non-major' risk factor = severe LV systolic dysfunction (e.g. LV EF < 40%), Hypertension, Diabetes mellitus, Female sex - Age 65–74 years, Vascular disease]

Until recently, the only OAC used was warfarin. Warfarin reduces stroke by ~60% and death by ~25% compared with no treatment. Despite its clinical efficacy, warfarin has multiple, well-known limitations, including numerous interactions with other drugs and the need for regular blood monitoring and dose adjustments. Thus, warfarin therapy may be underused or inappropriate for patients with atrial fibrillation.
In the past 10 years, novel drugs have been developed that may ultimately replace warfarin for patients with AF. The direct thrombin and factor Xa inhibitors overcome the need for routine blood monitoring, and the trial results have been encouraging overall. Three new drugs (apixaban, dabigatran, and rivaroxaban), all significantly reduce the risk of hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding into the brain) as compared with warfarin. Of the three drugs, only dabigatran at a dose of 150 mg holds the distinction of also having significantly reduced the risk of ischemic stroke (strokes caused by a blood clot) as compared with warfarin. Furthermore, the risk of particularly serious bleeding was reduced with each of the three drugs, as compared with warfarin.
Switching to a newer agent may not be necessary for the individual patient in whom the INR has been well controlled with warfarin for years. In addition, although the newer anticoagulants have a more rapid onset and termination of anticoagulant action than does warfarin, agents to reverse the effect of the drugs are still under development and are not routinely available. In addition, generic warfarin is expected to be markedly less expensive than the newer agents even after the costs associated with regular INR monitoring are considered. Thus, although the new drugs are attractive alternatives, it is likely that warfarin will continue to be used worldwide in many patients with AF.
An alternative way to prevent strokes would be to remove the pocket (i.e. the left atrial appendage) by surgery. This requires open-heart surgery where the circulation is maintained by using a heart bypass machine. Although theoretically possible this form of major heart surgery is not recommended.
The LAA can also be closed by a special device without the need for major surgery. A thin tube (catheter) is inserted into a vein in the top of the leg (the femoral vein) and guided into the left atrium. A special device or plug is moved up the catheter into place at the mouth of the LAA. This device stops any blood clots getting into the bloodstream. Placing the plug in this way is a lot easier on the patient than having open-heart surgery. The procedure is done in the cardiac catheterization laboratory using x-ray imaging and transoesophageal echo to guide the catheter that places the plug. The procedure takes about two hours to perform and is usually done under general anaesthesia. There are currently two devices available to close the LAA: the WATCHMAN™ and the Amplatzer Cardiac Plug ACP™. Both devices have a good track record in safety and efficacy and have been licensed in the UK for this procedure.

The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) has said that this procedure is safe enough and works well enough for use in the NHS. NICE has produced information on this procedure for patients and carers ('Understanding NICE guidance'). It explains the nature of the procedure and the guidance issued by NICE, and has been written with patient consent in mind. See www.nice.org.uk/guidance/IPG349/publicinfo
- You will need to stop warfarin therapy for 3 days if you are on it. Please continue with aspirin and/or clopidogrel if you are already taking these drugs.
- You must fast from 12 midnight the night beforeyour admission to hospital
- You will be admitted in to the hospital on the morning of the procedure
- The procedure will be explained to you again by your Cardiologist and you will meet the anaesthetist who will be performing the general anaesthesia
- You will be given aspirin and clopidogrel tablets ('blood thinners') if you are not already taking these drugs
- You will be given antibiotics to prevent any infections – please tell the doctors and nurses if you are allergic to any drugs.
- Once you are asleep with the anaesthetic, a transoesophageal echo probe is passed through the mouth into the oesophagus to image the heart
- The LAA will be examined carefully to make sure that there are no blood clots already in the pocket. If there is already a blood clot present we will be unable to proceed with the procedure as there is a risk the plug will dislodge the clot and cause a stroke. You will need to have a few weeks of anticoagulation (either warfarin or injections of heparin) to help the clots dissolve before we can try again.
- A short thin plastic tube (sheath) is placed into the femoral vein at the top of the right leg in the groin. A long plastic tube called a catheter is passed through the sheath to the heart and a special sharp needle is used to make a small hole in the atrial septum. This divides the right and left atrium and the hole will allow access to the left atrium and the LAA pocket.
- You will be given an injection of intravenous heparin to prevent any blood clots developing on the equipment during the procedure
- The device (Watchman™ or Amplatzer Cardiac Plug ™) is loaded into a special delivery catheter that is passed through the atrial septum and into the mouth of the LAA. The device is then deployed.
- When we have checked the device is stable and firmly fixed in the pocket the device is released from the catheter. The final position of the device is checked with the transoesophageal echo and the procedure is finished. The tubes will be removed from the groin.
- You will be observed in the monitoring area on the day ward briefly before being transferred to the main ward
- If there are no complications you may be discharged home the same day. You may be asked to stay in overnight.
- Access site complications – bleeding or bruising in the groin where the tubes have been inserted into the vein
- Cardiac perforation – this can occur at the time the small hole is made in the septum but the risks are minimized by using careful imaging with the transoesophageal echo; the catheter delivering the device can perforate the soft wall of the LAA, and the devices are anchored in the LAA with small hooks that may perforate the wall of the LAA – the risk of this is very small and you will be closely monitored during and after the procedure for any signs of leak. Blood collects in the pericardium (the sack covering the heart) and if there is a leak this can be drained with a small needle.
- Device migration and embolisation – the device is anchored in the LAA with small hooks that grasp the muscle in the wall of the pocket. If these hooks do not implant properly there is a possibility the device may move from the pocket. If this were to happen, the device would have to be retrieved with open heart surgery at which time the LAA would be removed as well. This occurred in less than 1% of patients in a large trial of 707 patients
- Blood clots on the device – during the procedure you will receive heparin to prevent blood clots forming on the metal of the device. After the procedure you will be required to take some 'blood-thinners' to help prevent clots. The Watchman™ device requires at least 6 weeks of treatment with warfarin after the device is implanted; after this your Cardiologist will discuss with you what is the best drug for you to remain on. The ACP™ device does not require warfarin, but instead aspirin for 6 months and clopidogrel for at least 1 month. The precise regimen for you will be discussed with you prior to discharge.
- Incomplete closure of the LAA – there is a small risk that the device will not seal the LAA entirely. While there is stiil a pocket there is a risk of blood clots and rarely patients have more than one device implanted.
Contact Us
01494 867 616
info@chilternheart.com
To book an appointment click here
